Чемпионат мира по мини-футболу 2020. Футбол чемпионат мира 2020
Франция примет чемпионат мира по футболу среди роботов в 2020 году - Экономика и бизнес
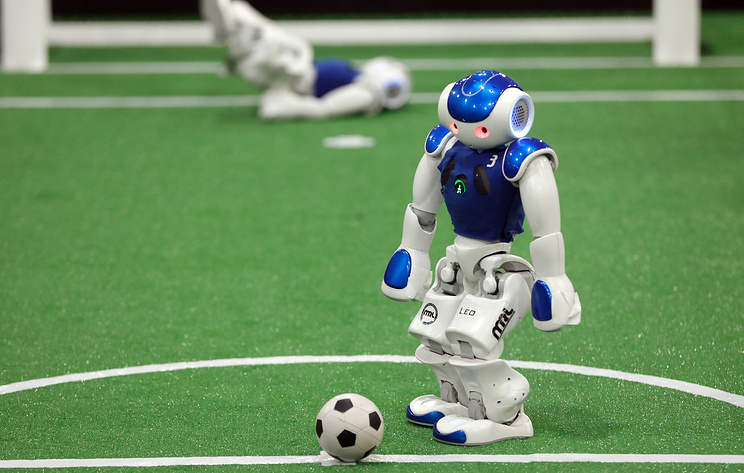

© EPA-EFE/ABEDIN TAHERKENAREH
ПАРИЖ, 19 июня. /Корр. ТАСС Михаил Тимофеев/. Чемпионат мира по футболу среди роботов пройдет в городе Бордо в 2020 году. Об этом сообщили агентству France Presse (AFP) организаторы мероприятия.
Согласно их данным, роботов-футболистов выставят на международные соревнования более четырех десятков стран. Город Бордо выбран неслучайно - именно на его территории расположена Бордосская лаборатория информационных исследований (Labri), занимающаяся, в частности, вопросами искусственного интеллекта и робототехникой. В ней была создана команда роботов небольших размеров (90-сантиметрового роста, так называемая категория Kid Size) Rhoban. В течение двух лет подряд (2016-2017) Бордосская лаборатория завоевывала с ней звание чемпиона мира по футболу в категории "разумной техники".
В понедельник кандидатура Бордо на проведение ЧМ-2020 была одобрена в Монреале, где открылся чемпионат 2018 года. Соревнования в Бордо в 2020 году станут 24-ми по счету в категории борьбы за кубок RoboCup. Им будут предшествовать игры в Австралии в 2019 году.
Во Франции кроме команды-чемпиона из Бордо существуют еще две - "Три мушкетера", участников которой создают в Университете Версаль-Сен-Кантен-ан-Ивелин, а также команда роботов при Инженерной высшей школе Лиона.
Первые соревнования роботов в игре в футбол на приз RoboCup (сокращение от Robot Soccer World Cup) были проведены группой из трех японских разработчиков робототехники еще в 1996 году. При этом они поставили перед инженерами всех стран задачу - создать высокоэффективную и полностью автономную в своих действиях футбольную команду роботов, которая к 2050 году должна обыграть реальную человеческую сборную в лице чемпиона мира. Причем с полным соблюдением правил FIFA.
Сейчас группы разработчиков встречаются на четырехдневных соревнованиях, в ходе которых их роботы не только соревнуются в футболе, но и демонстрируют свои способности в спасении людей в условиях природных катастроф и оказании различного рода помощи людям в домашних условиях.
Новости smi2.ru
Новости smi2.ru
Загрузка...
tass.ru
Чемпионат мира по мини-футболу 2020 Википедия
Чемпионат мира по мини-футболу 2020 (англ. 2020 FIFA Futsal World Cup) — 9-й Чемпионат мира по мини-футболу ФИФА.
Выборы места проведения
Кандидатами на принятие чемпионата мира по мини-футболу 2020 являются 7 стран:
- Коста-Рика
 Коста-Рика
Коста-Рика - Иран
 Иран
Иран - Япония
 Япония
Япония - Казахстан
 Казахстан
Казахстан - Литва
 Литва
Литва - Новая Зеландия
 Новая Зеландия
Новая Зеландия - ОАЭ
 ОАЭ
ОАЭ
Ни одна из этих стран ещё не принимала у себя Чемпионат мира. Также интерес к проведению чемпионата проявляли: Египет, Грузия, Чехия, Хорватия, Нидерланды и США. Выборы страны — хозяйки первенства мира должны были пройти в декабре 2016 года, но из-за антикоррупционных расследований в ФИФА их отложили на декабрь 2017.
Ссылки
- Чемпионат мира по мини-футболу на сайте ФИФА
|
wikiredia.ru
Чемпионат мира по мини-футболу 2020
1. ФИФА – The Fédération Internationale de Football Association is the international governing body of association football, futsal, and beach soccer. FIFA is responsible for the organisation of major international tournaments, notably the World Cup which commenced in 1930. FIFA was founded in 1904 to oversee international competition among the associations of Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden. Headquartered in Zürich, its membership now comprises 211 national associations, although FIFA does not control the rules of football, it is responsible for both the organization of a number of tournaments and their promotion, which generate revenue from sponsorship. In 2013, FIFA had revenues of over 1.3 billion U. S. dollars, for a net profit of 72 million and those among these officials who were also indicted in the U. S. are expected to be extradited to face charges there as well. Many officials were suspended by FIFAs ethics committee including Sepp Blatter, in early 2017 reports became public about FIFA president Gianni Infantino attempting to prevent the re-elections of both chairmen of the ethics committee during the FIFA congress in May 2017. The need for a body to oversee association football became apparent at the beginning of the 20th century with the increasing popularity of international fixtures. The French name and acronym are used even outside French-speaking countries, the founding members were the national associations of Belgium, Denmark, France, the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden and Switzerland. Also, that day, the German Association declared its intention of affiliating through a telegram. The first president of FIFA was Robert Guérin, Guérin was replaced in 1906 by Daniel Burley Woolfall from England, by then a member of the association. Membership of FIFA expanded beyond Europe with the application of South Africa in 1909, Argentina in 1912, Canada and Chile in 1913, and the United States in 1914. During World War I, with players sent off to war and the possibility of travel for international fixtures severely limited. Post-war, following the death of Woolfall, the organisation was run by Dutchman Carl Hirschmann and it was saved from extinction, but at the cost of the withdrawal of the Home Nations, who cited an unwillingness to participate in international competitions with their recent World War enemies. The Home Nations later resumed their membership, the FIFA collection is held by the National Football Museum at Urbis in Manchester, England. The first World Cup in the world was in 1930 in Montevideo, FIFA is headquartered in Zürich, and is an association established under the Law of Switzerland. FIFAs supreme body is the FIFA Congress, a made up of representatives from each affiliated member association. Each national football association has one vote, regardless of its size or footballing strength, the Congress assembles in ordinary session once every year, and extraordinary sessions have been held once a year since 1998. The congress makes decisions relating to FIFAs governing statutes and their method of implementation and application, only the Congress can pass changes to FIFAs statutes
2. Коста-Рика – It has a population of around 4.5 million, of whom nearly a quarter live in the metropolitan area of the capital and largest city, San José. Costa Rica was sparsely inhabited by people before coming under Spanish rule in the 16th century. Since then, Costa Rica has remained among the most stable, prosperous, following a brief civil war, it permanently abolished its army in 1949, becoming one of only a few sovereign nations without a standing army. Costa Rica is a member of the Organisation Internationale de la Francophonie. The country has consistently performed favourably in the Human Development Index, placing 69th in the world as of 2015 and its rapidly developing economy, once heavily dependent on agriculture, has diversified to include sectors such as finance, pharmaceuticals, and ecotourism. Costa Rica is known for its environmental policies, being the only country to meet all five UNDP criteria established to measure environmental sustainability. Costa Rica officially plans to become a country by 2021. In 2012, it became the first country in the Americas to ban recreational hunting, historians have classified the indigenous people of Costa Rica as belonging to the Intermediate Area, where the peripheries of the Mesoamerican and Andean native cultures overlapped. More recently, pre-Columbian Costa Rica has also described as part of the Isthmo-Colombian Area. The oldest evidence of occupation in Costa Rica is associated with the arrival of various groups of hunter-gatherers about 10,000 to 7,000 years BCE in the Turrialba Valley. The presence of Clovis culture type spearheads and arrows from South America opens the possibility that, in this area, agriculture became evident in the populations that lived in Costa Rica about 5,000 years ago. They mainly grew tubers and roots, for the first and second millennia BCE there were already settled farming communities. These were small and scattered, although the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture as the livelihood in the territory is still unknown. The earliest use of pottery appears around 2,000 to 3,000 BCE, shards of pots, cylindrical vases, platters, gourds and other forms of vases decorated with grooves, prints, and some modelled after animals have been found. The impact of indigenous peoples on modern Costa Rican culture has been small compared to other nations. Costa Rica was described as the poorest and most miserable Spanish colony in all America by a Spanish governor in 1719, for all these reasons, Costa Rica was, by and large, unappreciated and overlooked by the Spanish Crown and left to develop on its own. Costa Rica became a democracy with no oppressed mestizo or indigenous class. It was not long before Spanish settlers turned to the hills, where they found rich volcanic soil, like the rest of Central America, Costa Rica never fought for independence from Spain
3. Иран – Iran, also known as Persia, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, is a sovereign state in Western Asia. Comprising a land area of 1,648,195 km2, it is the second-largest country in the Middle East, with 82.8 million inhabitants, Iran is the worlds 17th-most-populous country. It is the country with both a Caspian Sea and an Indian Ocean coastline. The countrys central location in Eurasia and Western Asia, and its proximity to the Strait of Hormuz, Tehran is the countrys capital and largest city, as well as its leading economic and cultural center. Iran is the site of to one of the worlds oldest civilizations, the area was first unified by the Iranian Medes in 625 BC, who became the dominant cultural and political power in the region. The empire collapsed in 330 BC following the conquests of Alexander the Great, under the Sassanid Dynasty, Iran again became one of the leading powers in the world for the next four centuries. Beginning in 633 AD, Arabs conquered Iran and largely displaced the indigenous faiths of Manichaeism and Zoroastrianism by Islam, Iran became a major contributor to the Islamic Golden Age that followed, producing many influential scientists, scholars, artists, and thinkers. During the 18th century, Iran reached its greatest territorial extent since the Sassanid Empire, through the late 18th and 19th centuries, a series of conflicts with Russia led to significant territorial losses and the erosion of sovereignty. Popular unrest culminated in the Persian Constitutional Revolution of 1906, which established a monarchy and the countrys first legislative body. Following a coup instigated by the U. K. Growing dissent against foreign influence and political repression led to the 1979 Revolution, Irans rich cultural legacy is reflected in part by its 21 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, the third-largest number in Asia and 11th-largest in the world. Iran is a member of the UN, ECO, NAM, OIC. Its political system is based on the 1979 Constitution which combines elements of a democracy with a theocracy governed by Islamic jurists under the concept of a Supreme Leadership. A multicultural country comprising numerous ethnic and linguistic groups, most inhabitants are Shia Muslims, the largest ethnic groups in Iran are the Persians, Azeris, Kurds and Lurs. Historically, Iran has been referred to as Persia by the West, due mainly to the writings of Greek historians who called Iran Persis, meaning land of the Persians. As the most extensive interactions the Ancient Greeks had with any outsider was with the Persians, however, Persis was originally referred to a region settled by Persians in the west shore of Lake Urmia, in the 9th century BC. The settlement was then shifted to the end of the Zagros Mountains. In 1935, Reza Shah requested the international community to refer to the country by its native name, opposition to the name change led to the reversal of the decision, and Professor Ehsan Yarshater, editor of Encyclopædia Iranica, propagated a move to use Persia and Iran interchangeably
4. Япония – Japan is a sovereign island nation in Eastern Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies off the eastern coast of the Asia Mainland and stretches from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea, the kanji that make up Japans name mean sun origin. 日 can be read as ni and means sun while 本 can be read as hon, or pon, Japan is often referred to by the famous epithet Land of the Rising Sun in reference to its Japanese name. Japan is an archipelago consisting of about 6,852 islands. The four largest are Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu and Shikoku, the country is divided into 47 prefectures in eight regions. Hokkaido being the northernmost prefecture and Okinawa being the southernmost one, the population of 127 million is the worlds tenth largest. Japanese people make up 98. 5% of Japans total population, approximately 9.1 million people live in the city of Tokyo, the capital of Japan. Archaeological research indicates that Japan was inhabited as early as the Upper Paleolithic period, the first written mention of Japan is in Chinese history texts from the 1st century AD. Influence from other regions, mainly China, followed by periods of isolation, from the 12th century until 1868, Japan was ruled by successive feudal military shoguns who ruled in the name of the Emperor. Japan entered into a period of isolation in the early 17th century. The Second Sino-Japanese War of 1937 expanded into part of World War II in 1941, which came to an end in 1945 following the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Japan is a member of the UN, the OECD, the G7, the G8, the country has the worlds third-largest economy by nominal GDP and the worlds fourth-largest economy by purchasing power parity. It is also the worlds fourth-largest exporter and fourth-largest importer, although Japan has officially renounced its right to declare war, it maintains a modern military with the worlds eighth-largest military budget, used for self-defense and peacekeeping roles. Japan is a country with a very high standard of living. Its population enjoys the highest life expectancy and the third lowest infant mortality rate in the world, in ancient China, Japan was called Wo 倭. It was mentioned in the third century Chinese historical text Records of the Three Kingdoms in the section for the Wei kingdom, Wa became disliked because it has the connotation of the character 矮, meaning dwarf. The 倭 kanji has been replaced with the homophone Wa, meaning harmony, the Japanese word for Japan is 日本, which is pronounced Nippon or Nihon and literally means the origin of the sun. The earliest record of the name Nihon appears in the Chinese historical records of the Tang dynasty, at the start of the seventh century, a delegation from Japan introduced their country as Nihon
5. Казахстан – Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country in northern Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Kazakhstan is the worlds largest landlocked country, and the ninth largest in the world, Kazakhstan is the dominant nation of Central Asia economically, generating 60% of the regions GDP, primarily through its oil/gas industry. It also has vast mineral resources, Kazakhstan is officially a democratic, secular, unitary, constitutional republic with a diverse cultural heritage. Kazakhstan shares borders with Russia, China, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan, the terrain of Kazakhstan includes flatlands, steppe, taiga, rock canyons, hills, deltas, snow-capped mountains, and deserts. Kazakhstan has an estimated 18 million people as of 2014, Given its large area, its population density is among the lowest. The capital is Astana, where it was moved in 1997 from Almaty, the territory of Kazakhstan has historically been inhabited by nomadic tribes. This changed in the 13th century, when Genghis Khan occupied the country as part of the Mongolian Empire, following internal struggles among the conquerors, power eventually reverted to the nomads. By the 16th century, the Kazakh emerged as a distinct group, the Russians began advancing into the Kazakh steppe in the 18th century, and by the mid-19th century, they nominally ruled all of Kazakhstan as part of the Russian Empire. Following the 1917 Russian Revolution, and subsequent civil war, the territory of Kazakhstan was reorganised several times, in 1936, it was made the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, part of the Soviet Union. Kazakhstan was the last of the Soviet republics to declare independence during the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Kazakhstan has worked to develop its economy, especially its dominant hydrocarbon industry. Kazakhstans 131 ethnicities include Kazakhs, Russians, Uzbeks, Ukrainians, Germans, Tatars, the Kazakh language is the state language, and Russian has equal official status for all levels of administrative and institutional purposes. The name Kazakh comes from the ancient Turkic word qaz, to wander, the name Cossack is of the same origin. The Persian suffix -stan means land or place of, so Kazakhstan can be translated as land of the wanderers. Kazakhstan has been inhabited since the Neolithic Age, the regions climate, archaeologists believe that humans first domesticated the horse in the regions vast steppes. Central Asia was originally inhabited by the Scythians, the Cuman entered the steppes of modern-day Kazakhstan around the early 11th century, where they later joined with the Kipchak and established the vast Cuman-Kipchak confederation. Under the Mongol Empire, the largest in history, administrative districts were established. These eventually came under the rule of the emergent Kazakh Khanate, throughout this period, traditional nomadic life and a livestock-based economy continued to dominate the steppe. Nevertheless, the region was the focus of ever-increasing disputes between the native Kazakh emirs and the neighbouring Persian-speaking peoples to the south, at its height the Khanate would rule parts of Central Asia and control Cumania
6. Литва – Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in Northern Europe. One of the three Baltic states, it is situated along the shore of the Baltic Sea, to the east of Sweden. It is bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, Lithuania has an estimated population of 2.9 million people as of 2015, and its capital and largest city is Vilnius. The official language, Lithuanian, along with Latvian, is one of two living languages in the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. For centuries, the shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, the Lithuanian lands were united by Mindaugas, the King of Lithuania, and the first unified Lithuanian state, with the Lublin Union of 1569, Lithuania and Poland formed a voluntary two-state union, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Commonwealth lasted more than two centuries, until neighboring countries systematically dismantled it from 1772–95, with the Russian Empire annexing most of Lithuanias territory. As World War I neared its end, Lithuanias Act of Independence was signed on 16 February 1918, in the midst of the Second World War, Lithuania was first occupied by the Soviet Union and then by Nazi Germany. As World War II neared its end and the Germans retreated, Lithuania is a member of the European Union, the Council of Europe, a full member of the Eurozone, Schengen Agreement and NATO. It is also a member of the Nordic Investment Bank, the United Nations Human Development Index lists Lithuania as a very high human development country. Lithuania has been among the fastest growing economies in the European Union and is ranked 21st in the world in the Ease of Doing Business Index, the first people settled in the territory of Lithuania after the last glacial period in the 10th millennium BC. Over a millennium, the Indo-Europeans, who arrived in the 3rd – 2nd millennium BC, mixed with the local population, the first written mention of Lithuania is found in a medieval German manuscript, the Annals of Quedlinburg, in an entry dated 9 March 1009. Initially inhabited by fragmented Baltic tribes, in the 1230s the Lithuanian lands were united by Mindaugas, after his assassination in 1263, pagan Lithuania was a target of the Christian crusades of the Teutonic Knights and the Livonian Order. Despite the devastating century-long struggle with the Orders, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania expanded rapidly, by the end of the 14th century, Lithuania was one of the largest countries in Europe and included present-day Belarus, Ukraine, and parts of Poland and Russia. The geopolitical situation between the west and the east determined the multicultural and multi-confessional character of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the ruling elite practised religious tolerance and Chancery Slavonic language was used as an auxiliary language to the Latin for official documents. In 1385, the Grand Duke Jogaila accepted Polands offer to become its king, Jogaila embarked on gradual Christianization of Lithuania and established a personal union between Poland and Lithuania. It implied that Lithuania, the fiercely independent land, was one of the last pagan areas of Europe to adopt Christianity, after two civil wars, Vytautas the Great became the Grand Duke of Lithuania in 1392. During his reign, Lithuania reached the peak of its expansion, centralization of the state began
7. Новая Зеландия – New Zealand /njuːˈziːlənd/ is an island nation in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The country geographically comprises two main landmasses—the North Island, or Te Ika-a-Māui, and the South Island, or Te Waipounamu—and around 600 smaller islands. New Zealand is situated some 1,500 kilometres east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and roughly 1,000 kilometres south of the Pacific island areas of New Caledonia, Fiji, because of its remoteness, it was one of the last lands to be settled by humans. During its long period of isolation, New Zealand developed a distinct biodiversity of animal, fungal, the countrys varied topography and its sharp mountain peaks, such as the Southern Alps, owe much to the tectonic uplift of land and volcanic eruptions. New Zealands capital city is Wellington, while its most populous city is Auckland, sometime between 1250 and 1300 CE, Polynesians settled in the islands that later were named New Zealand and developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight New Zealand, in 1840, representatives of Britain and Māori chiefs signed the Treaty of Waitangi, which declared British sovereignty over the islands. In 1841, New Zealand became a colony within the British Empire, today, the majority of New Zealands population of 4.7 million is of European descent, the indigenous Māori are the largest minority, followed by Asians and Pacific Islanders. Reflecting this, New Zealands culture is derived from Māori and early British settlers. The official languages are English, Māori and New Zealand Sign Language, New Zealand is a developed country and ranks highly in international comparisons of national performance, such as health, education, economic freedom and quality of life. Since the 1980s, New Zealand has transformed from an agrarian, Queen Elizabeth II is the countrys head of state and is represented by a governor-general. In addition, New Zealand is organised into 11 regional councils and 67 territorial authorities for local government purposes, the Realm of New Zealand also includes Tokelau, the Cook Islands and Niue, and the Ross Dependency, which is New Zealands territorial claim in Antarctica. New Zealand is a member of the United Nations, Commonwealth of Nations, ANZUS, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Pacific Islands Forum, and Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation. Dutch explorer Abel Tasman sighted New Zealand in 1642 and called it Staten Landt, in 1645, Dutch cartographers renamed the land Nova Zeelandia after the Dutch province of Zeeland. British explorer James Cook subsequently anglicised the name to New Zealand, Aotearoa is the current Māori name for New Zealand. It is unknown whether Māori had a name for the country before the arrival of Europeans. Māori had several names for the two main islands, including Te Ika-a-Māui for the North Island and Te Waipounamu or Te Waka o Aoraki for the South Island. Early European maps labelled the islands North, Middle and South, in 1830, maps began to use North and South to distinguish the two largest islands and by 1907, this was the accepted norm. The New Zealand Geographic Board discovered in 2009 that the names of the North Island and South Island had never been formalised and this set the names as North Island or Te Ika-a-Māui, and South Island or Te Waipounamu
8. Объединённые Арабские Эмираты – In 2013, the UAEs population was 9.2 million, of which 1.4 million are Emirati citizens and 7.8 million are expatriates. The country is a federation of seven emirates, and was established on 2 December 1971, the constituent emirates are Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras al-Khaimah, Sharjah and Umm al-Quwain. Each emirate is governed by a monarch, together, they jointly form the Federal Supreme Council. One of the monarchs is selected as the President of the United Arab Emirates, Islam is the official religion of the UAE and Arabic is the official language. The UAEs oil reserves are the seventh-largest in the world while its natural gas reserves are the worlds seventeenth-largest, Sheikh Zayed, ruler of Abu Dhabi and the first President of the UAE, oversaw the development of the Emirates and steered oil revenues into healthcare, education and infrastructure. The UAEs economy is the most diversified in the Gulf Cooperation Council, while its most populous city of Dubai is an important global city, nevertheless, the country remains principally reliant on its export of petroleum and natural gas. The UAE is criticised for its rights record, including the specific interpretations of Sharia used in its legal system. The UAEs rising international profile has led analysts to identify it as a regional. It appears the land of the Emirates has been occupied for thousands of years, there is no proof of contact with the outside world at that stage, although in time it developed with civilisations in Mesopotamia and Iran. This contact persisted and became wide-ranging, probably motivated by trade in copper from the Hajar Mountains, in ancient times, Al Hasa was part of Al Bahreyn and adjoined Greater Oman. Sassanid groups were present on the Batinah coast, in 637, Julfar was an important port that was used as a staging post for the Islamic invasion of the Sassanian Empire. The area of the Al Ain/Buraimi Oasis was known as Tuam and was an important trading post for camel routes between the coast and the Arabian interior. The earliest Christian site in the UAE was first discovered in the 1990s, a monastic complex on what is now known as Sir Bani Yas Island. Thought to be Nestorian and built in 600 AD, the church appears to have been abandoned peacefully in 750 AD and it forms a rare physical link to a legacy of Christianity which is thought to have spread across the peninsula from 50 to 350 AD following trade routes. Certainly, by the 5th century, Oman had a bishop named John – the last bishop of Oman being Etienne, in 676 AD. This led to a group of travelling to Medina, converting to Islam and subsequently driving a successful uprising against the unpopular Sassanids. Following the death of Prophet Muhammad, the new Islamic communities south of the Persian Gulf threatened to disintegrate, with insurrections against the Muslim leaders. The Caliph Abu Bakr sent an army from the capital Medina which completed its reconquest of the territory with the battle of Dibba in which 10,000 lives are thought to have been lost
9. Египет – Egypt, officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia by a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. Egypt is a Mediterranean country bordered by the Gaza Strip and Israel to the northeast, the Gulf of Aqaba to the east, the Red Sea to the east and south, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. Across the Gulf of Aqaba lies Jordan, and across from the Sinai Peninsula lies Saudi Arabia, although Jordan and it is the worlds only contiguous Afrasian nation. Egypt has among the longest histories of any country, emerging as one of the worlds first nation states in the tenth millennium BC. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt experienced some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, urbanisation, organised religion and central government. One of the earliest centres of Christianity, Egypt was Islamised in the century and remains a predominantly Muslim country. With over 92 million inhabitants, Egypt is the most populous country in North Africa and the Arab world, the third-most populous in Africa, and the fifteenth-most populous in the world. The great majority of its people live near the banks of the Nile River, an area of about 40,000 square kilometres, the large regions of the Sahara desert, which constitute most of Egypts territory, are sparsely inhabited. About half of Egypts residents live in areas, with most spread across the densely populated centres of greater Cairo, Alexandria. Modern Egypt is considered to be a regional and middle power, with significant cultural, political, and military influence in North Africa, the Middle East and the Muslim world. Egypts economy is one of the largest and most diversified in the Middle East, Egypt is a member of the United Nations, Non-Aligned Movement, Arab League, African Union, and Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. Miṣr is the Classical Quranic Arabic and modern name of Egypt. The name is of Semitic origin, directly cognate with other Semitic words for Egypt such as the Hebrew מִצְרַיִם, the oldest attestation of this name for Egypt is the Akkadian
10. Грузия – Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. The capital and largest city is Tbilisi, Georgia covers a territory of 69,700 square kilometres, and its 2016 population is about 3.72 million. Georgia is a unitary, semi-presidential republic, with the government elected through a representative democracy, during the classical era, several independent kingdoms became established in what is now Georgia. The kingdoms of Colchis and Iberia adopted Christianity in the early 4th century, a unified Kingdom of Georgia reached the peak of its political and economic strength during the reign of King David IV and Queen Tamar in the 12th and early 13th centuries. Thereafter the kingdom declined and eventually disintegrated under hegemony of various powers, including the Mongols, the Ottoman Empire. Russian rule over Georgia was eventually acknowledged in various treaties with Iran. Since the establishment of the modern Georgian republic in April 1991, post-communist Georgia suffered from civil, the countrys Western orientation soon led to the worsening of relations with Russia, culminating in the brief Russo-Georgian War in August 2008. Georgia is a member of the United Nations, the Council of Europe, and it contains two de facto independent regions, Abkhazia and South Ossetia, which gained limited international recognition after the 2008 Russo-Georgian War. Georgia and a part of the international community consider the regions to be part of Georgias sovereign territory under Russian military occupation. Georgia probably stems from the Persian designation of the Georgians – gurğān, in the 11th and 12th centuries adapted via Syriac gurz-ān/gurz-iyān, starting with the Persian word gurğ/gurğān, the word was later adopted in numerous other languages, including Slavic and West European languages. This term itself might have established through the ancient Iranian appellation of the near-Caspian region. The self-designation used by ethnic Georgians is Kartvelebi, the medieval Georgian Chronicles present an eponymous ancestor of the Kartvelians, Kartlos, a great-grandson of Japheth. However, scholars agree that the word is derived from the Karts, the name Sakartvelo consists of two parts. Its root, kartvel-i, specifies an inhabitant of the core central-eastern Georgian region of Kartli, ancient Greeks and Romans referred to early western Georgians as Colchians and eastern Georgians as Iberians. Today the full, official name of the country is Georgia, before the 1995 constitution came into force the countrys name was the Republic of Georgia. The territory of modern-day Georgia was inhabited by Homo erectus since the Paleolithic Era, the proto-Georgian tribes first appear in written history in the 12th century BC. The earliest evidence of wine to date has found in Georgia. In fact, early metallurgy started in Georgia during the 6th millennium BC, the classical period saw the rise of a number of early Georgian states, the principal of which was Colchis in the west and Iberia in the east
wikivisually.com










